Additive manufacturing with Laser revolutionizes manufacturing technology
Additive manufacturing with Laser, also known as Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) or Laser-based 3D printing, is a revolutionary manufacturing technology. It uses a Laserbeam to apply or melt material layer by layer to create three-dimensional objects.
Advantages of additive manufacturing with Laser (LAM)
Various materials can be used in additive manufacturing with Laser, including metals, plastics, ceramics and even biological tissue. The choice of material depends on the requirements of the application.
Design freedom
Laser Additive manufacturing (LAM) enables the production of complex geometries that are difficult or otherwise impossible to manufacture.
Efficiency
As only the material that is actually needed is used, LAM can be very material and resource efficient.
Speed
Additive manufacturing with Laser produces prototypes and components in a short time, which shortens the time to market.
Cost reduction
Costs can often be saved by manufacturing components with less material and without complex tools.
How do we support you with additive manufacturing?
Selecting the right Lasersystem components plays a decisive role in the success and efficiency of additive manufacturing. For example, you can positively influence the speed of the process by selecting the galvo scanner or improve the accuracy of the material application by choosing the nozzle.
By consulting the experts at Innotech Laser , you can be sure that you are choosing exactly the Lasercomponents for additive manufacturing that best meet your expectations.
You also benefit from our know-how, as we already support a considerable customer base in this industry with our products.
Advantages:
- First-class advice on the selection of Laser for AM
- Benefit from our wealth of experience
- Tailor-made solutions thanks to a wide range of products
- Attractive prices for our Laser components
- Technical support and maintenance of our products
"Choosing the right Laserproducts is crucial for success and competitiveness. We are happy to help you select suitable Laserproducts for additive manufacturing."
Maximilian Abeln, Innotech Laser GmbH
Typical applications in additive manufacturing with Laser 3D printing
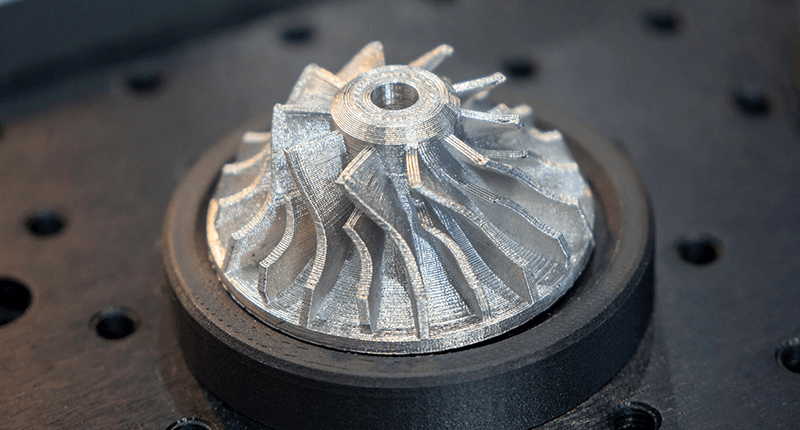

Metal 3D printing (SLM)
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is a special additive manufacturing technique for metals that makes it possible to produce complex metal parts by melting metal powder layer by layer.
Most frequently selected configuration for metal 3D printing (SLM)

Raycus fiberlaser RFL-C200AM

Galvo scanner innoSCAN II-14

Laser Optics F-Theta 1064 nm Fused Silica

Plastic 3D printing (FDM/FFF)
Plastic 3D printing, also known as fused deposition modeling (FDM) or fused filament fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing technique in which plastic filaments are heated and applied layer by layer to produce three-dimensional objects.
Most frequently selected configuration for plastic 3D printing (FDM/FFF)

Raycus fiberlaser RFL-C200AM

Galvo scanner innoSCAN II-14

Laser Optics F-Theta 1064 nm Fused Silica

Additive manufacturing in medical technology
The additive manufacturing of ceramics in medical technology has gained considerable importance in recent years, as it offers the possibility of producing complex ceramic components and implants.
Most frequently selected configuration for additive manufacturing in medical technology

Raycus fiberlaser RFL-C500AM

Galvo scanner innoSCAN II-16

Laser Optics F-Theta 1064 nm Fused Silica
Let us advise you and test how good our Lasersystems are
If you have any questions, need a quote or would like to test a configuration in our technical center, please send us an e-mail or simply give us a call. We will answer you as quickly as possible.
Contact us
Address
Innotech Laser GmbH
Giesenheide 31
40724 Hilden
Germany
Office hours
Monday to Thursday
08:30 am to 5:00 pm
Friday
08:30 am to 4:00 pm
Further applications
Laser cutting
Laser systems are tools that are low-wear and versatile. They are therefore used in almost all industries for cutting materials, hard or soft.
More about cutting with laser
Laser cleaning
Cleaning surfaces with Laser technology offers numerous application possibilities in various industries.

Laser battery production
Laser can cut, engrave and weld materials such as lithium and graphite with micrometer precision. Ideal for battery cell production.
